How to Install and Secure phpMyAdmin with Apache on CentOS 7
Published on
•4 min read

phpMyAdmin is an open-source PHP based tool for managing MySQL and MariaDB servers over a web-based interface.
phpMyAdmin allows you to interact with MySQL databases, manage user accounts and privileges, execute SQL-statements, import and export data in a variety of data formats and much more.
In this tutorial, we will walk through the steps necessary for installing and securing phpMyAdmin with Apache on CentOS 7.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have met the following prerequisites before continuing with this tutorial:
- LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) installed on your CentOS server .
- Logged in as a user with sudo privileges .
Although not necessary, it is advised to access your phpMyAdmin installation over HTTPS. If you don’t have SSL on your sites, follow the instructions about securing your Apache with Let’s Encrypt on CentOS 7 .
Installing phpMyAdmin
To install phpMyAdmin on a CentOS 7 system perform the following steps:
phpMyAdmin is not available in CentOS 7 core repositories. To install phpMyAdmin we need to enable the EPEL repository first:
sudo yum install epel-releaseOnce the EPEL repository is enabled we can install phpMyAdmin and all of it’s dependencies with the following command:
sudo yum install phpmyadmin
Configuring and Securing phpMyAdmin
Apache configuration file for phpMyAdmin is created automatically during the installation. By default all connections except those from localhost are denied. Since we will be accessing phpMyAdmin from remote locations we need to modify the configuration file and specify allowed IP addresses.
Open the phpMyAdmin Apache configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.confChange the two lines that read Require ip 127.0.0.1 with your home connection’s IP address. If you don’t know your home IP address open Google search in your web browser and type what is my ip.
# Apache 2.4
<RequireAny>
Require ip 192.168.42.57
Require ip ::1
</RequireAny>Close and save the file.
Require all granted before the Require ip line.For an extra layer of security we’ll password protect the phpMyAdmin directory by setting up a basic authentication.
Start by creating a new authentication file using the htpasswd tool. We will store the .htpasswd file in /etc/phpMyAdmin directory:
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/phpMyAdmin/.htpasswd adminIn this example we are creating a user named admin. You can choose any username you want.
The command above will prompt you to enter and confirm the user’s password.
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user admin
Later, if you need to add additional users, use the same command without the -c flag:
sudo htpasswd /etc/phpMyAdmin/.htpasswd admin2The next step is to configure Apache to password protect the phpMyAdmin directory and use the .htpasswd file. To do so open the phpMyAdmin.conf file which was automatically created during the phpMyAdmin installation:
sudo nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/phpMyAdmin.confAnd insert the following lines highlighted in yellow:
<Directory /usr/share/phpMyAdmin/>
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8
Options +FollowSymLinks +Multiviews +Indexes
AllowOverride None
AuthType basic
AuthName "Authentication Required"
AuthUserFile /etc/phpMyAdmin/.htpasswd
Require valid-user
<IfModule mod_authz_core.c>
...Save the file and restart the Apache service for changes to take effect:
sudo systemctl restart httpd/phpmyadmin alias to something more unique and secure.When accessing your phpMyAdmin, you will be prompted to enter the login credentials of the user you previously created:
https://your_domain_or_ip_address/phpmyadmin
After entering the basic authentication, you’ll be taken to the phpMyAdmin login page where you need to enter your MySQL administrative user login credentials.
Accessing phpMyAdmin
To access the phpMyAdmin interface open your favorite browser and type your server’s domain name or public IP address followed by /phpmyadmin:
https://your_domain_or_ip_address/phpmyadmin
Enter the administrative user login credentials you previously created and click Go.
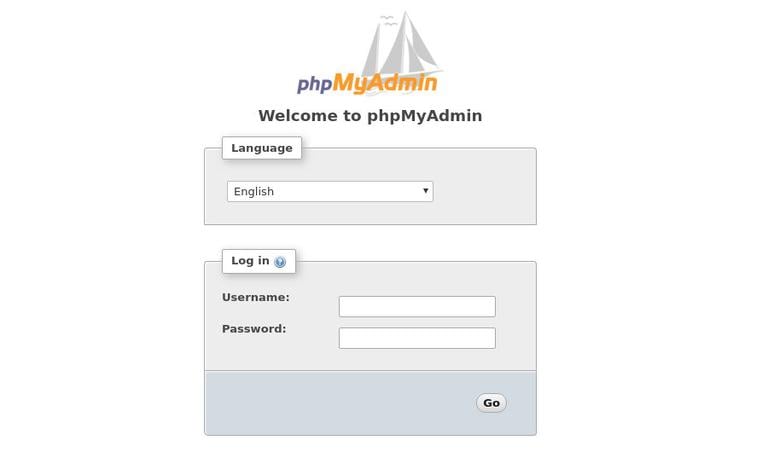
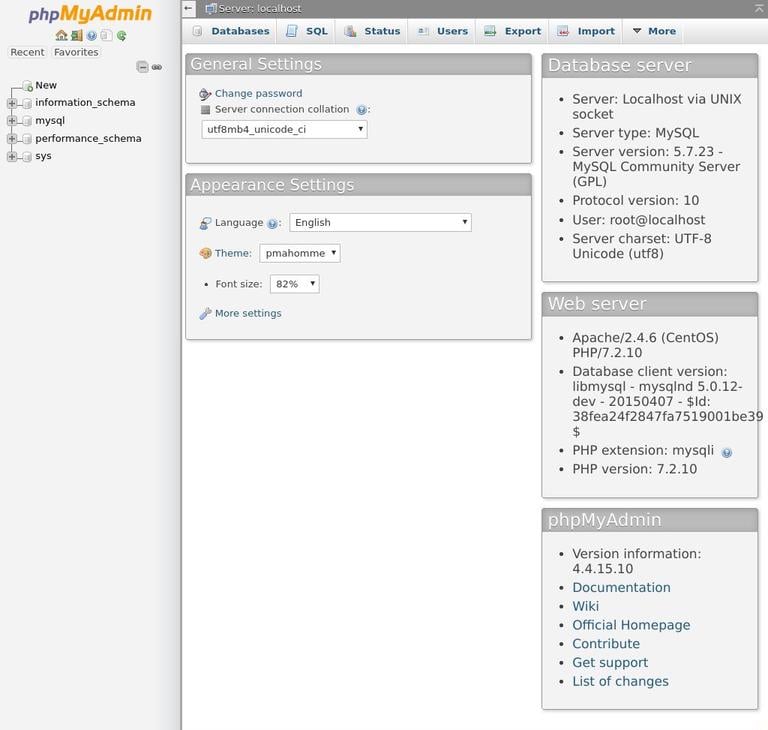
Once you log in, you’ll see the phpMyAdmin dashboard, which will look something like this:
Conclusion
Congratulations, you have successfully installed phpMyAdmin on your CentOS 7 server. You can now start creating MySQL databases, users and tables and perform various MySQL queries and operations.
If you have questions, feel free to leave a comment below.


